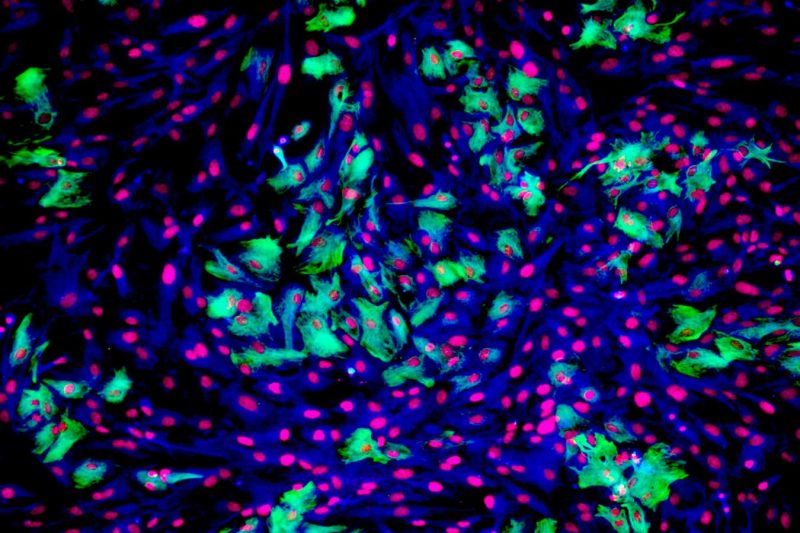
A new type of brain cell has been discovered, called a glutamatergic astrocyte. This type of cell could potentially explain the development of neurodegenerative conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
Traditionally, brain cells are categorized into two types: neurons and glia. Neurons communicate with each other through synapses, while glia do not use this type of signaling.
However, two decades ago, Andrea Volterra and his colleagues discovered that certain glia could also use synaptic-like transmission to communicate with other cells. This finding was initially met with controversy, but now, a different research team has used modern techniques to confirm the existence of this communication method.
The researchers analyzed gene production data in mouse cells to look for protein complexes involved in synaptic transmission in cells other than neurons. They specifically focused on cells in the hippocampus region of the brain. The analysis revealed clusters of astrocytes, a type of glia, that appeared to possess the ability to participate in synaptic transmission. These cells were found to release the neurotransmitter glutamate, which is the most common neurotransmitter in the brain. The researchers referred to these cells as glutamatergic astrocytes.
The researchers then used two-photon imaging to study glutamate release in the brains of mice and confirmed that the signals emitted by these cells were similar in speed to neurons. They also found similar protein signatures of synaptic transmission in non-neuronal cells in humans.
The purpose of glia communicating via synaptic transmission is still unclear, but it suggests that it could lead to a greater coordination of signals in the brain. One astrocyte can connect with thousands or millions of synapses, allowing signals to spread more effectively and efficiently.
These newly discovered cells also seem to be involved in brain circuits related to movement, which is significant in the context of Parkinson’s disease. Understanding these cells could potentially provide insights into the treatment and management of the condition.