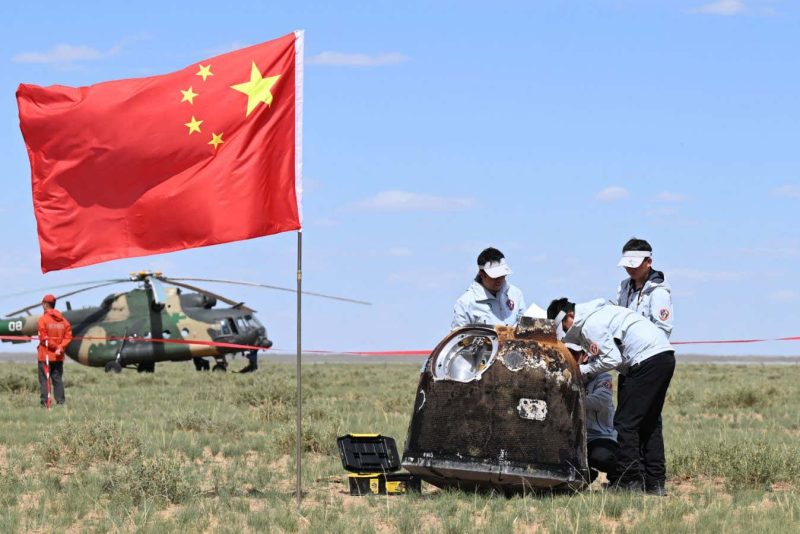
The Chang’e 6 probe being retrieved in Siziwang Banner in Interior Mongolia, China
Xinhua/Shutterstock
China’s Chang’e 6 spacecraft has returned to Earth, bringing again the primary chunks of house rock from the far aspect of the moon.
The capsule touched down in Siziwang Banner in Interior Mongolia, China, on 25 June, after separating from an orbiting container 5000 kilometres above the Atlantic Ocean at about 1:20pm native time.
The pattern, which ought to comprise round 2 kilograms of fabric from the moon, then floated down for the final 10 kilometres utilizing parachutes. It landed at 2:07pm earlier than being collected by scientists from the China Nationwide House Administration.
The issue of touchdown on the moon’s far aspect, which completely faces away from Earth and so has no direct communications hyperlink, had meant that the area’s floor was unexplored till the Chinese language spacecraft landed firstly of the month.
Its touchdown and assortment manoeuvres relied closely on autonomous processes and robotic instruments, though Chinese language engineers may ship messages to the spacecraft by way of the Queqiao-2 relay satellite tv for pc, which launched in March this 12 months and remains to be in orbit across the moon.
The pattern accommodates materials from the floor and from 2 metres underground, which Chang’e 6 drilled and scooped at its touchdown website within the Apollo crater, itself located throughout the bigger South Pole-Aitken basin. Scientists hope that this materials will assist clarify how and when these basins fashioned, which may enable us to know the origin of different, related lunar craters.
The rock might also point out the amount of water ice within the area, which may very well be a significant useful resource for crewed missions that China hopes to ship to the moon by 2030.
Earlier than China undertakes a crewed mission, it can ship an additional two spacecraft, Chang’e 7 and Chang’e 8, to the moon’s south pole to assemble info on places for a attainable base there referred to as the Worldwide Lunar Analysis Station. China is co-leading this mission together with Russia’s house company, Roscosmos.
Subjects: